Conditions
Conditions allow you to perform actions based on certain conditions. This is what makes a program “intelligent” and makes it make decisions.
In programming, we use
If - Do - Otherwise
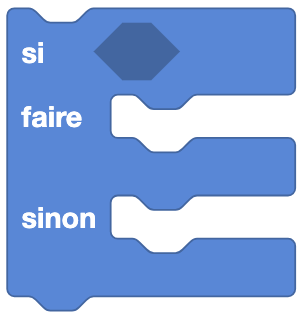
Type: Order
Definition :
This block allows you to perform an action if a condition is true, and another action if the condition is false. It is composed of three parts:
- If: the condition to check (if it is true, we execute the
Doblock, this is called a boolean). - Do: the block of instructions to execute if the condition is true.
- Else: the block of instructions to execute if the condition is false.
Use :
If we want Eliobot to move forward if a sensor detects an obstacle, and to move backwards if no obstacle is detected.
If - Do
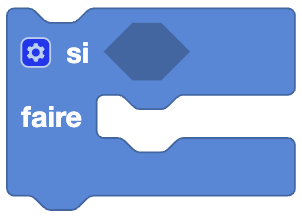
This block uses the same logic as the If - Do - Else block but with one specificity: we can modify the block to add additional conditions using the gear.
Editing the block
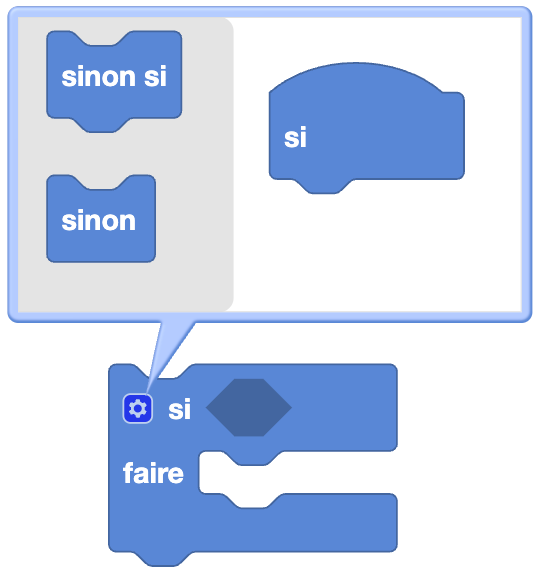
Type: Order
Definition :
Here you can stack as many conditions as you want. If all conditions are true, then the Do part of the block is executed.
All conditions are checked one by one in the order they are stacked. If a condition is false, the Do block is not executed.
Use :
If we want Eliobot to move forward if a sensor detects an obstacle, and to move backwards if no obstacle is detected, but also for the robot to stop if another sensor detects an obstacle.
Example
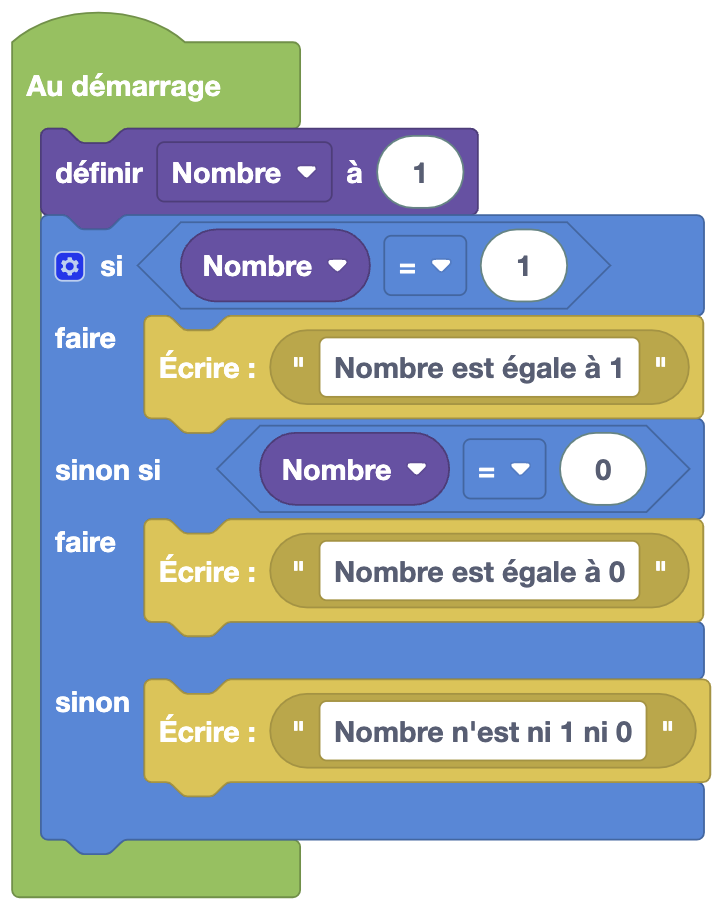
In this example, only the first condition will be executed because it is the first in the list that is true. If the first condition had been false, then the second condition would have been true, and if this had also been false, the 'else' block would have intervened, acting when none of the previous conditions are true.
Comparison
Type: Boolean block
Definition :
This block allows you to compare two values. It is composed of two parts:
- First value and second value: the values to compare.
- Comparison operator: the type of comparison to perform (equal, different, greater, less, greater or equal, less or equal).
Use :
If we want to know if two values are equal, if one value is greater than another, etc.
Logical operation
Type: Boolean block
Definition :
This block allows you to perform a logical operation between two conditions. It is composed of two parts:
- First condition and second condition: the conditions to compare.
- Logical operator: the type of logical operation to perform (AND, OR).
Use :
If we want to know if two conditions are true or if one condition is true.
No
Type: Boolean block
Definition :
This block allows you to negate a condition. This means that no matter the condition, if it is true, it will become false and vice versa.
Use :
If we want to change a condition from true to false or vice versa.
True / False
Type: Boolean block
Definition :
This block allows you to define a Boolean value. This means that the value is either true or false.
Use :
If we want to define a starting condition.
Null
Type: Value
Definition :
This block allows you to define a zero value. This means that the value is not defined. Null is often used to mean that a variable has no value or is not defined.
Be careful, the zero value is not the same as the zero value.
Use :
If we want to define a variable without giving it a value.
Test
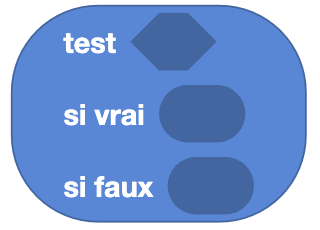
Type: Value
Definition :
This block allows you to test a condition. It is composed of two parts:
- Condition: the condition to be tested.
- Value to use: Depending on the result of the condition, the value to use.
Use :
If we want to test a condition and use a different value depending on the result.
Example
Learn how to use conditions in the following example: